Data privacy and security are more valuable than ever in our digital age, impacting individuals and organizations at every turn. The rising number of cyber threats means that protecting sensitive information is not only a regulatory requirement but also a fundamental aspect of maintaining trust and ensuring the smooth operation of businesses. This guide will explore the core forms of data privacy and security and offer practical advice to secure your data in the age of cyber threats.
Understanding Data Privacy and Security
Data privacy involves securing personal information from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. Everyone should have the power to decide how their data is collected, used, and shared. On the other hand, data security focuses on the measures and technologies used to protect data from breaches, cyberattacks, and other unauthorized access.
Together, data privacy and security form the basis of data protection strategy. They ensure that sensitive information, such as personal data, financial records, or proprietary business information, remains secure and is used in compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
The Growing Importance of Data Privacy
In recent years, data privacy has become a big concern due to numerous high-profile data breaches and the implementation of strict data protection laws. Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States have established new standards for how organizations manage personal data.
These regulations not only levy hefty fines for non-compliance but also grant individuals greater control over their personal information. Businesses are accountable for collecting, storing, and leveraging data, making data privacy a crucial element of corporate supervision.
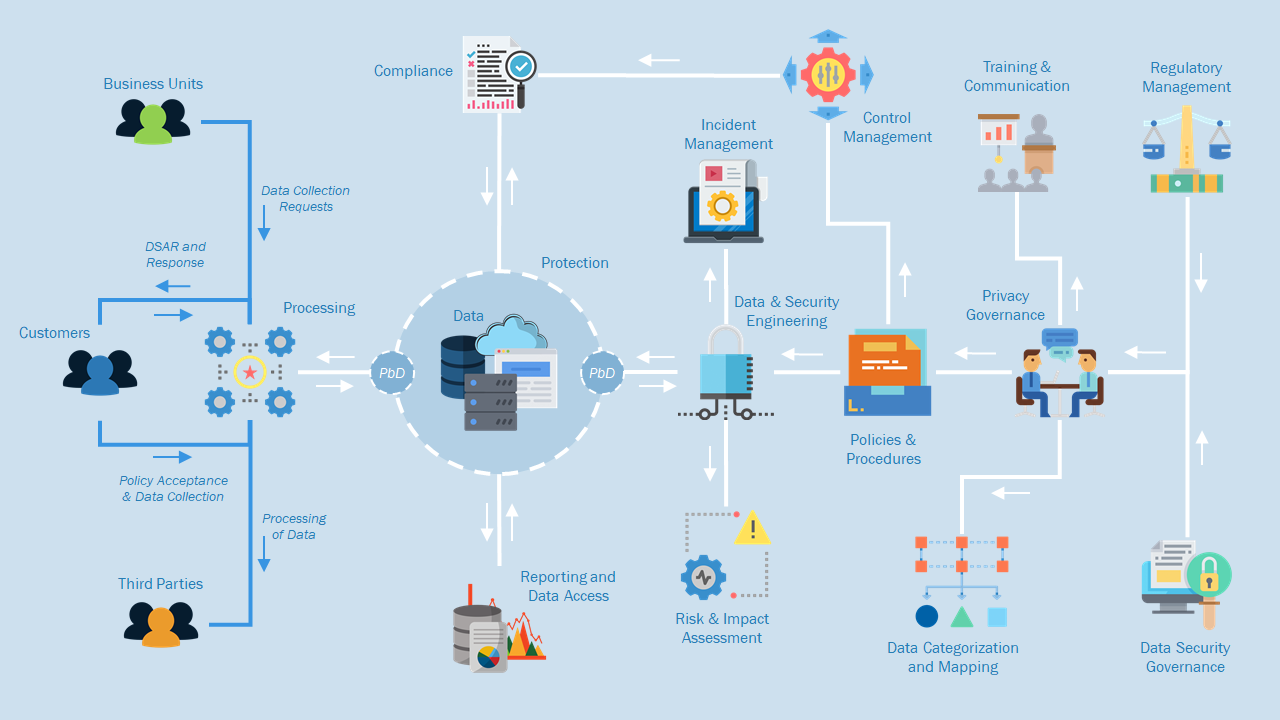
Core Principles of Data Privacy
To effectively protect personal data, organizations must adhere to several core principles:
Transparency: Inform individuals how their data is collected, used, and shared. It includes providing accessible privacy policies and obtaining explicit consent where required.
Data Minimization: Collect the data that is necessary for a specific purpose. Avoid gathering excessive information that could increase the risk of a breach.
Purpose Limitation: Remember to only use people's data for the reasons you collected it. If you want to use the data for new reasons, you need to get permission from the people about their data.
Data Accuracy: Ensure that personal data is accurate and up-to-date. Implement mechanisms for individuals to correct or update their information.
Storage Limitation: Retain personal data only for as long as necessary to fulfill the purpose for which it was collected. Securely delete or anonymize data that is no longer needed.
Security: Implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, loss, or destruction.
The Evolving Threat Landscape
As the digital landscape evolves, so do the threats to data privacy and security. Cybercriminals are constantly developing new techniques to exploit susceptibility in systems and steal sensitive information. Some of the most common cyber threats include:
Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals use deceptive emails or messages to trick individuals into revealing personal information, such as passwords or credit card numbers.
Ransomware: Malicious software that encrypts a victim's data, rendering it inaccessible until a ransom is paid.
Insider Threats: Employees or contractors with access to sensitive data may intentionally or unintentionally cause data breaches.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Sophisticated, targeted cyberattacks that infiltrate a network and remain undetected for extended periods, gathering valuable data.
Zero-Day Exploits: Cyberattacks target vulnerabilities in software that are unknown to the vendor and unpatched.
Best Practices for Data Security
To defend against these threats, organizations must adopt a comprehensive data security strategy that includes the following best practices:
Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access. Strong encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable to unauthorized users.
Access Controls: Implement strict access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel have an approach to sensitive data. Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC) to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits, including penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and compliance checks, to identify and address vulnerabilities before cybercriminals can exploit them.
Incident Response Plan: Develop a robust incident response plan that outlines the steps taken in the event of a data breach or cyberattack. It should include procedures for containing the breach, notifying affected parties, and recovering from the incident.
Employee Training: Educate employees on the importance of data privacy and security. Provide regular training on recognizing phishing attempts, following best practices for password management, and understanding their role in protecting sensitive information.
Data Backup: Regularly back up critical data to ensure that it can be restored in the case of a ransomware attack or other data loss incidents. Ensure that backups are stored securely and not connected to the primary network.
The Role of Technology in Data Protection
Technology plays a crucial role in safeguarding data privacy and security. Several tools and technologies can help organizations protect their data, including:
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions: DLP tools monitor and control the flow of sensitive data within an organization, preventing unauthorized access or transfer.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: SIEM systems collect and analyze security-related data across the network, providing real-time threat detection and response capabilities.
Endpoint Protection: Endpoint protection solutions secure individual devices such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets from malware, phishing, and other threats.
Cloud Security: As more organizations move their data to the cloud, cloud security solutions protect data stored in cloud environments, including encryption, access controls, and monitoring.
Compliance and Legal Considerations
Compliance with data protection laws and regulations is a core aspect of privacy and security. Organizations must stay up-to-date with the latest legal requirements and ensure that their data protection practices align with the relevant regulations.
Failure to comply with data protection laws can result in significant penalties, legal action, and damage to an organization's reputation. It's essential to work with legal and compliance experts to navigate the complex landscape of data protection regulations.
The Human Element in Data Privacy
It's important to remember that while technology is crucial for data protection, the human element should not be underestimated. Employees play a critical role in ensuring data privacy and security. By promoting a culture of data safety within the organization, businesses can minimize the risk of human error and insider threats.
Encouraging security awareness among employees, promoting ethical data handling practices, and establishing clear data protection policies are all core steps in creating a secure data environment.
Conclusion
Amidst the prevalence of cyber threats, ensuring data privacy and security has become increasingly crucial. Organizations must adopt a proactive approach to safeguard sensitive information, comply with data protection regulations, and establish trust with their customers and stakeholders.
By embracing the best practices outlined in this guide, utilizing the latest technologies, and cultivating a culture of data security, businesses can establish a robust framework for securing their data. In doing so, they not only reduce the risk of cyber threats but also position themselves as responsible and reliable guardians of sensitive information.

Dot Labs is a leading IT outsourcing firm renowned for its comprehensive services, including cutting-edge software development, meticulous quality assurance, and insightful data analytics. Our team of skilled professionals delivers exceptional nearshoring solutions to companies worldwide, ensuring significant cost savings while maintaining seamless communication and collaboration. Discover the Dot Labs advantage today!
Visit our website: www.dotlabs.ai, for more information on how Dot Labs can help your business with its IT outsourcing needs.
For more informative Blogs on the latest technologies and trends click here