In the digital age, where data powers decisions, innovation, and business growth, privacy and security are paramount. Organizations must prioritize protecting sensitive information while adhering to stringent regulations. Building privacy-first architectures is not just about mitigating risks but fostering trust and ensuring compliance with evolving laws like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA. This blog explores what privacy-first architecture entails, why it matters, and how businesses can adopt it to stay ahead in the data-driven world.
What is Privacy-First Architecture?
A privacy-first architecture is a design philosophy that embeds privacy principles at the core of every system, application, and process within an organization. It goes beyond reactive measures to proactively safeguard data throughout its lifecycle.
This approach emphasizes:
Data Minimization: Collect only the data that is necessary.
Anonymization and Encryption: Ensure data is unreadable or untraceable without proper authorization.
Transparency: Let users know how their information is used and seek explicit consent.
Compliance Automation: Embed mechanisms that are compliant with regulatory requirements from the outset.
Why Privacy-First Architectures Matter?
Regulatory Compliance
Data privacy laws such as GDPR, CCPA, and many more require organizations to have a robust approach to data protection. Non-compliance would incur heavy fines and reputation damage.
Users are now much more aware of how their data is handled. A privacy-first approach creates trust, improves brand reputation, and encourages customer loyalty.
Risk Mitigation
Data breaches and cyberattacks lead to financial and operational losses. Privacy-first architectures minimize the vulnerabilities by design.
Competitive Advantage
Companies that take the lead in prioritizing privacy often outshine the competition and attract customers who value security and transparency.
Core Principles of Privacy-First Architecture
Privacy by Design and Default
This principle, named by Ann Cavoukian, ensures that privacy is the default for systems and processes. All features workflows or components must be designed to respect privacy at design time.
Data Sovereignty
Ensure data is kept in jurisdictions where local and global regulations regarding data residency are respected.
Role-Based Access Control
Only allow access to data by authorized personnel. It minimizes insider threats and accidental exposure of data.
Auditable Trails
Implement logging and monitoring systems to track data access and modifications for accountability and breach detection.
Steps to Building Privacy-First Architectures
Understand Data Privacy Regulations
Familiarize yourself with the data privacy regulations, including GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act). Conduct regular audits to ensure compliance.
Map Your Data Flow
Identify what data you collect, where it is stored, and how it moves between systems. It helps in pinpointing vulnerabilities and ensuring end-to-end protection.
Implement Secure Data Collection Practices
Collect only necessary data (data minimization).
Data is collected only based on consent.
Avoid PII when anonymized data can be used.
Prioritize Encryption
Sensitive data should be encrypted at rest and in motion, both using strong encryption standards and by use of secure key management practices to avoid unauthorized decryption.
Anonymization and Pseudonymization
Remove identifiable markers from the datasets. This is especially important for analytics and data-sharing purposes where there must be the preservation of privacy.
Automate Compliance
Implement tools that help monitor and enforce compliance on the fly. Examples include Data Loss Prevention (DLP) software and automated consent management platforms.
Train Employees
Educate your workforce on privacy best practices, phishing threats, and maintaining data confidentiality.
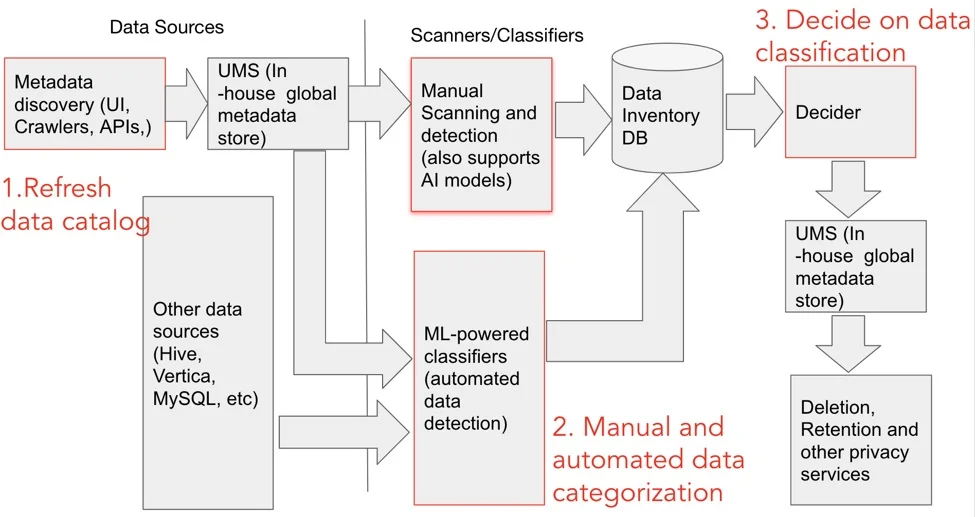
Privacy First Data Architecture
Enabling Technologies for Privacy-First Architectures
Blockchain
Immutable ledgers will ensure data transparency and integrity, making them ideal for audit trails and verifying data authenticity.
Zero-Trust Security Models
Trust nobody by default. Authenticate and authorize every access request based on the least privilege.
AI-Driven Privacy Tools
Use machine learning to detect anomalies and automate consent management with built-in compliance at scale.
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
Integrate networking and security to protect distributed teams and remote work locations.
Building Privacy-First Architectures Challenges
Usability vs Privacy
Striking a balance between the desirability of an application and stringent privacy requirements is challenging.
Regulatory Changes
Maintaining adaptability with shifting laws is difficult and even updating systems in response to new regulations.
Operational Costs
The penalty of power for strong privacy is that it is very resource-intensive, especially for smaller companies.
Legacy Systems
Legacy systems are expensive to upgrade to fit the privacy-first principles.
Case Studies: Privacy-First in Action
Case Study 1: Apple's App Tracking Transparency
Its App Tracking Transparency is a privacy first step. It allows users to decide whether an app can track them across other companies' apps and websites.
Case Study 2: GDPR Compliance for an E-commerce Platform
An online retailer overhauled its systems to comply with GDPR by deploying cookie consent banners, data encryption, and a streamlined process for data deletion requests.
Future of Privacy-First Architectures
AI and Privacy
AI can enable smarter privacy solutions, such as predictive compliance monitoring and anomaly detection. However, ethical AI usage must also be prioritized.
Edge Computing
Processing data closer to its source minimizes data exposure, enhancing privacy and reducing latency.
Universal Privacy Frameworks
Efforts are underway to create universal standards for privacy to simplify global compliance challenges.
Conclusion
Building privacy-first architectures is no longer optional; it’s a necessity in today’s interconnected world. By adopting a proactive approach, businesses can protect user data, foster trust, and stay ahead in an era of stringent data regulations.
Take the first stride toward a culture of privacy. Start small, prioritize compliance, and continually evolve to ensure your systems are robust and ready for the future. Because, as the saying goes - "prevention is better than cure" in data security and compliance.

Dot Labs is a leading IT outsourcing firm renowned for its comprehensive services, including cutting-edge software development, meticulous quality assurance, and insightful data analytics. Our team of skilled professionals delivers exceptional nearshoring solutions to companies worldwide, ensuring significant cost savings while maintaining seamless communication and collaboration. Discover the Dot Labs advantage today!
Visit our website: www.dotlabs.ai, for more information on how Dot Labs can help your business with its IT outsourcing needs.
For more informative Blogs on the latest technologies and trends click here