What
Are Data Silos?
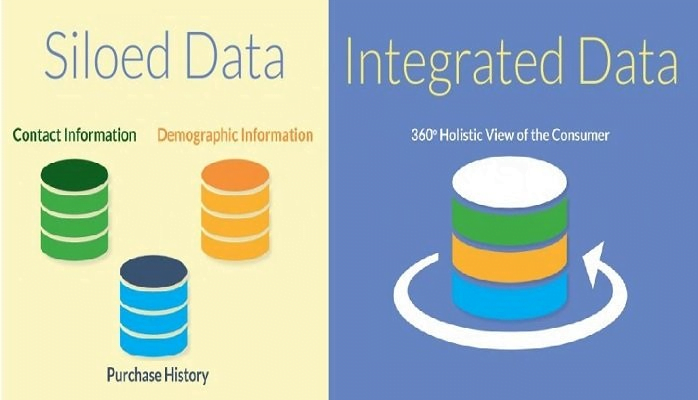
So,
what are data silos? Data silos are a term often used in IT, referring to
a situation where only a few individuals in an organization have access to
specific data or information that is not available or accessible to
others. It is like storing a few valuable resources in a vault that can
only be unlocked by a few.
This has created a lot of inefficiencies over
the years because the data needed to make informed decisions by the different
involved individuals may not be available to them. This makes it
difficult for businesses to promote collaboration and an open working
environment.
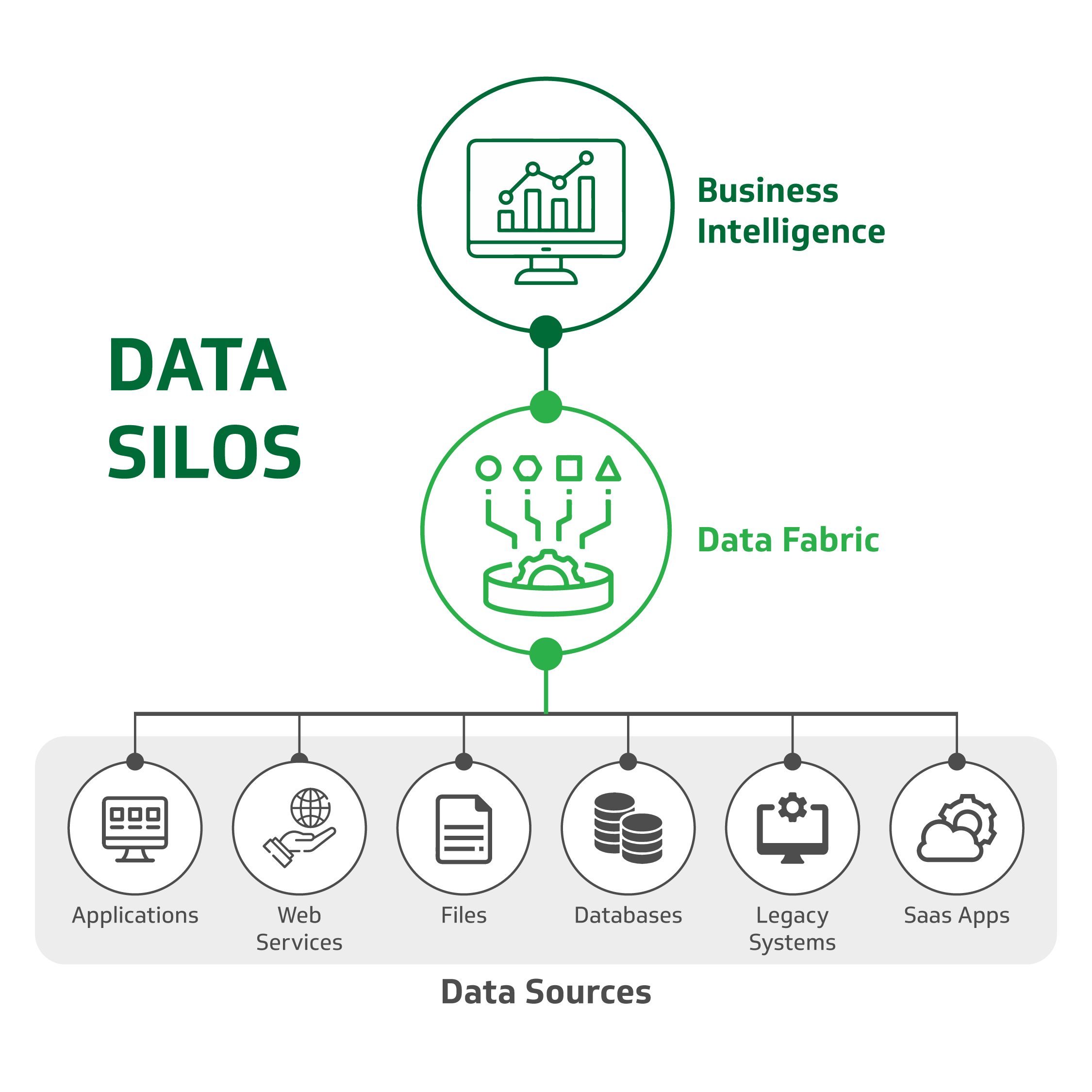
Data Silos in Mid-Market Businesses
Data
silos have been a common problem for mid-market businesses,
where data is often stored and managed by individual departments or
teams. This can lead to data being duplicated, inconsistent, or
outdated. It can also create barriers to communication and collaboration
between different departments. This can significantly hinder business
growth and success in a fast-paced business environment where data constantly
changes.
How
Data Silos Form?
Data
silos in organizations don’t just appear overnight; they are often the result
of various factors that compound over time. Understanding these factors
is key to recognizing and addressing the issue in any business setting.
Data silos typically
emerge due to a combination of factors, including:
Organizational Structure
In
many businesses, especially those with traditional hierarchical structures,
departments operate as individual units. This structure often leads to
each team focusing solely on its goals and data needs, working in isolation
from the rest of the company. For instance, the marketing department might
collect and analyze customer data independently of the sales or service
departments, leading to fragmented customer insights.
Such
a siloed approach can be particularly pronounced in larger organizations where
communication between departments is more challenging due to size and
complexity.
Legacy Systems
Legacy
systems, older software, or hardware systems cannot often integrate with newer
technologies. These systems were usually designed for specific, isolated
functions and not for a modern, interconnected IT environment. For
example, a legacy CRM system might be unable to share data with a new
cloud-based sales platform, leading to disjointed customer data management.
The
challenge with legacy systems is their incompatibility with new technologies
and the cost and complexity involved in updating or replacing legacy systems.
Rapid Growth or Mergers
Organizations
that experience rapid growth or undergo mergers and acquisitions frequently
encounter data silo issues. This growth can lead to a patchwork of IT
systems and processes. For example, when two companies merge, each brings
its data systems and processes, often resulting in a complex, disjointed IT
infrastructure.
The
difficulty in such scenarios is integrating the existing data systems in a way
that is efficient and minimizes disruption to ongoing operations.
Cultural Barriers
Sometimes,
the root of data silos is not technological but cultural. There can be a
reluctance to share information between departments due to internal
competition, lack of trust, or fear of losing control over valuable data.
For instance, a sales team might hesitate to share customer insights with the
marketing team, fearing it could diminish their perceived importance with the
internal organization.
Overcoming
these cultural barriers often requires a shift in mindset and leadership
approach, emphasizing collaboration and transparency.
Specialized Software Solutions
Departments
often select software that best meets their needs without considering how it
will integrate with other systems used in the organization. For instance,
the finance department might use accounting software that doesn’t integrate
well with the HR department’s payroll system. This lack of integration
can lead to inconsistencies and inefficiencies in data handling across the
organization.
The
challenge here is to balance the need for specialized software with the broader
need for integration and data sharing.
Lack of a Coordinated Data Strategy
The
absence of a unified approach to data management is a significant contributor
to the formation of data silos. Without a coordinated strategy, disparate
systems and practices emerge, leading to disjointed data handling. For
example, without a clear data governance policy, different departments might
store and manage data in incompatible formats or systems, making it challenging
to aggregate and analyze data organization-wide.
A
coordinated data strategy involves setting organization-wide data collection,
storage, and sharing standards, ensuring data practices align with the overall
business objectives.
From
the nascent stages of computing, technology has served as the foundation for
data aggregation and analysis, fueling insights and empowering informed
decision-making. Today, with advanced analytics, cloud fortresses, and
artificial intelligence (AI) at our disposal, these technological solutions
have morphed into a more dynamic and robust force.
These cutting-edge instruments equip businesses with a panoramic and holistic
view of their data landscape, enabling them to demolish silos, unearth hidden
gems within the data, and establish a single source of truth. By harnessing the
formidable power of these advanced technologies, organizations can unlock a
treasure trove of new opportunities, make data-driven choices, and propel
themselves ahead in the ever-more-competitive digital arena.
Surveying the Technological Landscape
Before
delving into specific solutions, embarking on a journey through the
technological landscape is essential. Understanding the available tools and
platforms is a crucial first step in devising a strategy to conquer data silos.
The key elements to explore in this landscape are:
Data Integration
Platforms: Data integration
platforms are purpose-built systems designed to harmoniously combine data from
various sources, offering a unified and coherent view. These platforms serve as
the linchpin in the battle against data fragmentation, facilitating the
blending of data from databases, cloud services, applications, and more. The
result is a holistic perspective that enables informed decision-making.
Middleware Solutions: Middleware acts as the bridge
between disparate systems, acting as a translator that allows them to
communicate effectively. This technology plays a crucial role in ensuring that
data from various sources can interact seamlessly, making it an invaluable tool
in the quest to break down data silos. Middleware solutions help standardize
data formats, enable real-time data exchange, and enhance overall system
interoperability.
Cloud Services: Cloud-based platforms have
revolutionized the data storage and analytics landscape. They offer scalable
and flexible environments that can accommodate the evolving needs of mid-market
businesses. Cloud services not only provide efficient data storage but also
facilitate advanced analytics and data processing capabilities, making them a
compelling option for those seeking to escape the confines of on-premises data
silos.
Choosing the Right Tools
Selecting
the right technological tools is a mission-critical endeavor, and it involves
carefully considering various factors. To ensure a successful integration strategy,
mid-market businesses must weigh the following key considerations:
Compatibility: The chosen technology
solutions must seamlessly integrate with existing systems and infrastructure.
The goal is to avoid creating further silos while enhancing data accessibility
and usability. Compatibility ensures a smooth transition and minimizes disruption
to ongoing operations.
Scalability: In a rapidly evolving business
environment, scalability is paramount. The selected technology must have the
capacity to grow in tandem with the organization’s expanding data needs. This
adaptability ensures that the solution remains effective as data volumes and
complexity increase.
User-Friendliness: Technology solutions should be
user-friendly, ensuring that non-technical users can easily access and utilize
them. Promoting widespread adoption across the organization hinges on providing
intuitive interfaces and straightforward tools that empower employees to
leverage data effectively.
Strategies for seam-less Implementation
Implementing
new technology should be a well-thought-out and strategic process to maximize
success. To ensure a smooth integration and minimize disruptions, consider the
following strategies:
Phased Rollout: Implementing technological
solutions in stages can help manage the transition effectively. By breaking the
process into manageable phases, businesses can address challenges
incrementally, allowing for adjustments and reducing the risk of system-wide
issues.
Training and Support: Comprehensive training and
support are essential components of a successful technology implementation
strategy. Employees need the skills and knowledge to leverage the new tools
effectively. Providing training programs and accessible support resources
ensures that the workforce can adapt seamlessly.
Data Migration
Policies: Establishing
clear and robust data migration policies is crucial to maintaining data
integrity and security during the transition to new systems. These policies
should outline procedures for migrating data, ensuring that it is transferred
accurately, consistently, and securely.
Overcoming Common Challenges
While
technology holds immense potential in breaking down data silos, it is not
without its challenges. Mid-market businesses may encounter several hurdles
during the integration process, including:
Legacy Systems: Updating or integrating old
systems that are deeply embedded in business processes can be a complex task.
Legacy systems may lack compatibility with modern technologies, requiring
careful planning and, in some cases, phased transitions.
Data Quality: Ensuring that the integrated
data is clean, accurate, and consistent is paramount. Poor data quality can
undermine the effectiveness of any technological solution. Data governance
practices and data cleansing processes are essential to maintain data
integrity.
Change Management: Managing the human element of
technological change is critical. Resistance to change, fear of job
displacement, and uncertainty about the benefits of new technology can hinder
adoption. Effective change management strategies are essential to secure buy-in
and a smooth transition.
Monitoring and
Maintenance: The
journey does not end with technology implementation; it continues with ongoing
monitoring and maintenance. To sustain an integrated data environment,
continuous efforts are necessary to ensure that systems operate correctly, data
remains integrated, and the technology evolves with the organization’s needs.
Regular maintenance and updates are essential to keep systems in sync and
running smoothly.
By
leveraging the power of technology and adopting a strategic approach,
mid-market businesses can overcome these obstacles and successfully break free
from the constraints of data silos. A unified data landscape empowers them to
make data-driven decisions, optimize operations, and gain a competitive edge in
the ever-evolving digital landscape.

Dot Labs is an IT
outsourcing firm that offers a range of services, including software
development, quality assurance, and data analytics. With a team of skilled
professionals, Dot Labs offers nearshoring services to companies in North
America, providing cost savings while ensuring effective communication and
collaboration.
Visit our website: www.dotlabs.ai, for more information on how Dot
Labs can help your business with its IT outsourcing needs.
For more informative Blogs on the latest technologies and trends click here